The Blockchain 2.0 solution for data management of decentralised data storages in compliance with the EU GDPR
Our unique selling point is the basis for being able to delete and change data on a public, decentralized blockchain. Until now, this has only been possible in closed systems on private blockchains, which extremely limits the possible applications. We have now, for the first time, created the basis to be able to fulfill the strict rules of the EU GDPR on a public blockchain by actually deleting the data.
For the first time, this capability allows a dynamic blockchain to be used publicly, outside of closed areas for data management. Unlike a traditional blockchain that acts as an “addition-only” store, where data is merely added endlessly for eternity, we can also delete or modify that data.
This opens the way to map real, decentralized data management on a public blockchain to drive, for example, the digitization and networking of public institutions or companies. At the same time, individual persons can connect to it in the public space, who have full insight into the data stored about them at any time thanks to this newly created transparency.
Likewise, a customer or citizen is guaranteed full self-control over his or her data, which he or she can also delete or change at any time if necessary. This feature in particular will still play a major role in the implementation and enforcement of the new Online Access Act.
White-label services can be used in an uncomplicated manner via API. You can find our prototype including detailed documentation at https://www.bonebits.net
Backbonechain and limbchain
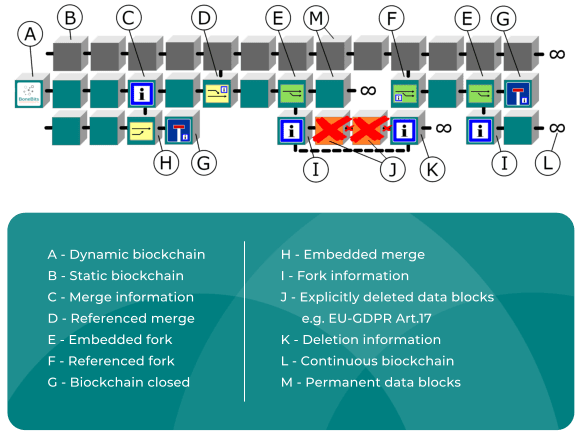
The procedure developed by us regarding the dynamic management of decentralised, based on blockchain data storages, extends the known properties of the blockchain by the dynamic properties of a database. Through privileged nodes, an independent ecosystem is capable first to finally end processes on a blockchain and to delete data blocks in areas which are specifically designated for that while maintaining the blockchain integrity. These dynamic properties are documented permanently and transparently on the blockchain. Optionally, the blockchains are as well directly forked or merged by linking or referencing. It is possible thanks to an individual task assignment of the network nodes and the declaration of new block types as well as the use of a new architecture of backbonechains and limbchains.
Their cooperation creates further features like the use of Blackbox, a network which is resistant against forking with dynamically distributed hash power as well as a free choice of script or programming language. By the dynamization of the ecosystem also the known scalability and power requirement problems are among others optimized by this procedure. By the procedure, maintaining its certain properties, the current application of the blockchain as a continuous “add only storage” becomes a dynamic, manageable, decentralised data storage and opens many new application areas which until now were possible only with help of native database applications. The almost infinite application possibilities resulting from that offer the interested universities and innovative market participants a significant advantage in an exciting market sector thanks to an “Education” or “Early Adopter” licence.

Dynamic Blockchain
Static Blockchain
Network

Erasable block

Finally deleted data
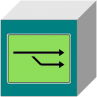
Embedded fork
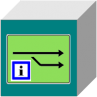
Referenced fork
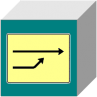
Embedded merge
Referenced merge
Information block
End of the blockchain
Advantages of our dynamic blockchain management
Thanks to the developed by us procedure for dynamization of the blockchain and its ecosystem, the decentralised data management receives a new value through new features. This is particularly important in the application areas and tasks like
- Access and management of the commonly used data
- Atoring the personal data
- Documentation obligations and exercising the statutory deletion deadlines
- Avoidance of data waste after the order conclusion
- Future-oriented, flexible, quick, private or public requirements
Access and management of the commonly used data
Data have to be protected in a decentralised way by a secure procedure and nonetheless be changeable. The authorised users have to have access to the same data pool.
Storing the personal data
Requirements of the UE GDPR like right of access by the data subject (article 15), right of rectification (article 16), right to erasure/to be forgotten (article 17) or the right to data portability (article 20) have to be able as personal data to be deleted or changed and the person concerned has to have the possibility to access their stored personal data. At the same time, the data portability has to be also reproduced transparently.
Documentation obligations and exercising the statutory deletion deadlines
Data pools from the continuous documentations with statutory deletion deadlines have to be able to be deleted upon the expiry of the time period.
Avoidance of data waste after the order conclusion
Data which are important only while an order is being processed, in order to avoid the accumulation of data waste, in particular also in view of “big data” have not to be kept longer. They have to be deleted.
Future-oriented, flexible, quick, private or public
Different data types have various requirement with regard to storage place, type or access and processing. Data have to be also possible to use in hybrid environments. The processing of these date has to be as well possible during the storage process, independently from the script or programming language, if necessary also in private environments. The free choice of requested script and programming languages makes middleware unnecessary and it keeps the system open also for future new languages. It is economic and reduces the risk of error in the whole system.
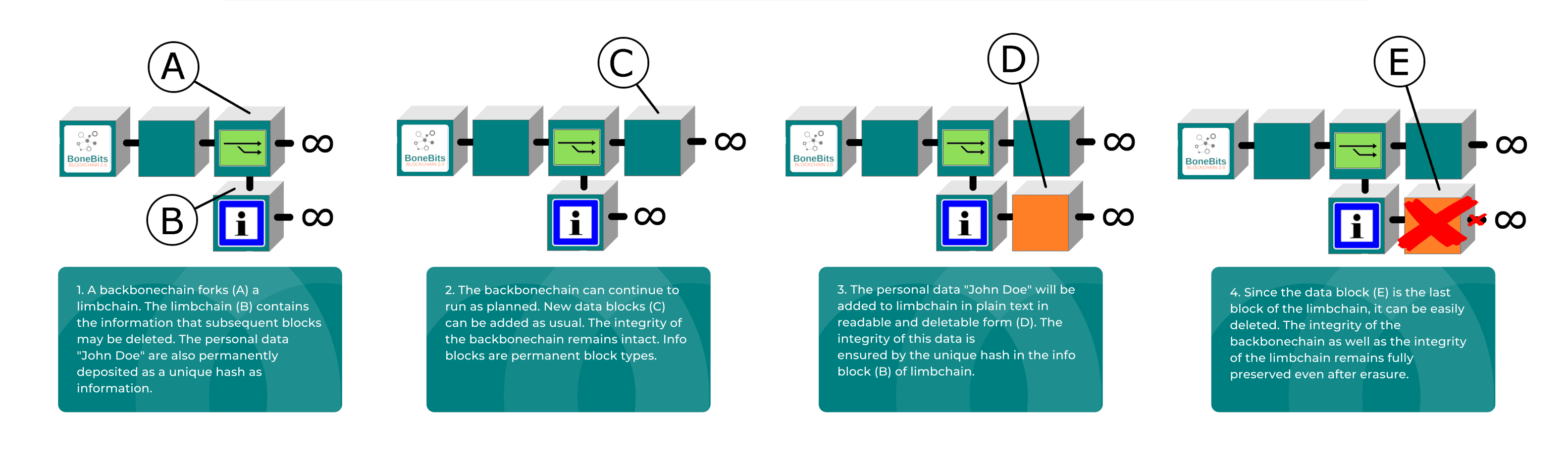
Deleting data on the blockchain
For data which have to remain changeable, from a backbonechain a limbchain is forked. In such formed new blockchain the erasability property as well as consent for executing the task was implemented in the procedure logic upon its generation. All data blocks which are added to this block may be deleted from back to front. If necessary, data block may be added once more. Data from the past may be discarded by excluding the expired periods and not be stored further.
Blockchain fork process
Should a new blockchain with other procedural logic required, it may be provided directly in the network without adjustment process. The authorised person decides whether a fork is required, not the network. The network remains without network splitting and it is able to process different blockchains with various procedural logic. In this way, the scalability as well as the energy requirement for the processing may by influenced directly. Referenced forks may take place at any data block, also retrospectively, if the blockchain itself run already further.
By that there may be forked
- Dynamic blockchain (embedded or referenced)
- Static blockchains (referenced)
In this way, it is among other things possible to continue smoothly the static blockchain processes on a dynamic blockchain. Dynamic blockchains do not have to be obligatorily embedded for forking. A pure referencing is also possible.
Merge process
Should several blockchains be merged into one blockchain, they may be connected with each other through a merge block for further running. Such linked blockchains may optionally run further parallel or be finally ended in order to run further as a merged blockchain.
By that there may be merged
- dynamic blockchains (embedded or referenced)
- static blockchains (referenced)
Therefore it is possible to connect suppliers for a product before the production process and to document the production itself together with the delivered suppliers’ components in a transparent production process. Dynamic blockchains do not have to be obligatorily embedded for merging. A pure referencing is also possible.
Informing
Many possibilities in dynamic processes require information. In order to ensure also here the transparency, pure information blocks may be implemented in the appropriate places of the blockchain. They are of pure information nature. The examples for it are
- Deletion information
- Merge information
- Fork information
- Individual information
Thus a permanent information may be deposited in important places at any time.
Finally end
First blockchains may be finally ended by adding an end block. Until now, the blockchains were always permanently running. The ending of the blockchain is applied in case of
- Ending the finally concluded processes
- Ending the procedure due to a change of the procedural logic
- Ending a blockchain due to merge
The authorisation for attaching and the appropriate consent for adding an end block is initially determined in the procedural logic of the blockchain. The information regarding the process are deposited directly in the end block.
Decentralised data storages generally
Decentralised data storages are characterised in particular by that, that they make available extremely high capacities thanks to their distributed architecture. Malfunctions due to natural disasters or cyberattacks are safely intercepted thanks to the high localisation redundancy. At the same time, they offer the highest transparency for the documentation requirements because thanks to a repeatedly controlled, neutral environment a trust with regard to the data integrity is ensured and it can be examined at any time.
Static Blockchain (storing only)
Visually regarded, the static blockchain is solidly anchored in the genome of the dynamic blockchain and its ecosystem. The good properties like
- Trust
- Integrity
- Safety
- Redundancy
- Transparency
- Decentralisation
- Revision safety
have been directly transmitted to it and remain also there as fixed properties of the permanent data blocks.
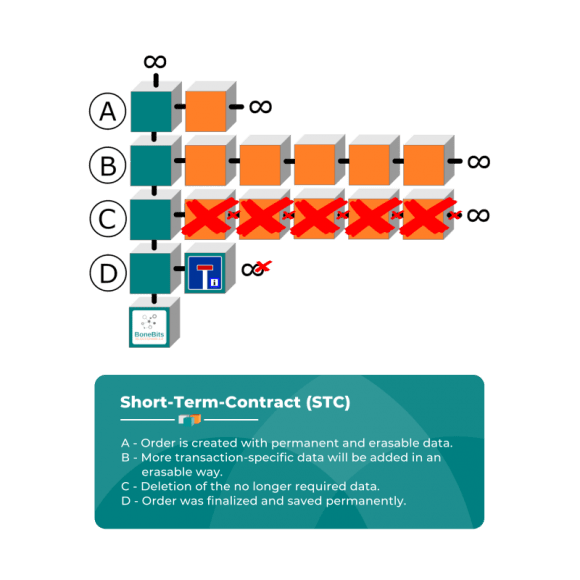
Short-Term Contracts (STC)
For processing, IoT and big data processes with short term collect personal or relating to processing data. After an successful execution, these data are not necessary anymore and have to be erased.
A STC applies in case of carrying out a Shipment Tracking, a Smart Car Park or Car and Ride Sharing.
Shipment Tracking
In the shipment tracking it is among other things about the letter and parcel services, forwarding, freight transport, shipping and goods, delivery and containers management.
- A – order created, shipper and consignee registered as deletable data.
- B – delivery stations until final delivery added in a deletable way.
- C – after expiry of the protest deadline, the personal and relating to the processing delivery data are erased.
- D – order was finally completed and stored permanently with the success relevant information on the blockchain.
Smart Car Park
The STCs may be also well applies in the IoT area. With that, the created here “Big Data” may be very easily managed.
- A – parking process created, the registration number identified as personal data and collected in a deletable way.
- B – day and time of arrival and of departure are added in a deletable way.
- C – after expiry of the protest deadline, the personal and the parking process data relating to the processing are erased.
- D – order was finally completed and stored permanently with the success relevant information on the blockchain.
Ride and Car Sharing
Here the decentralised data storage may be used directly through the apps. The status of the rental process is available immediately and clearly.
- A – rental process created, the client data identified as personal data and collected in a deletable way
- B – departure and return added in a deletable way.
- C – after expiry of the protest deadline, the personal and the rental process data relating to the processing are erased.
- D – order was finally completed and stored permanently with the success relevant information on the blockchain.
Therefore, the application list is not final and it may be used for all other, shortly running application purposes (refuelling, goods tracking, Smart Home etc.).
From the use of the aforementioned Short-Term Contracts (STC) the following advantages result:
- Personal data were deleted
- Data relating to the processing were deleted (no unnecessary data waste)
- Clear access of all participants to the process (online/app)
- Process carried out in a decentralised way without costs for maintaining, personnel, purchase and use of the own infrastructure (server/colocation/computing centre)
- Automatic resources scaling by the network
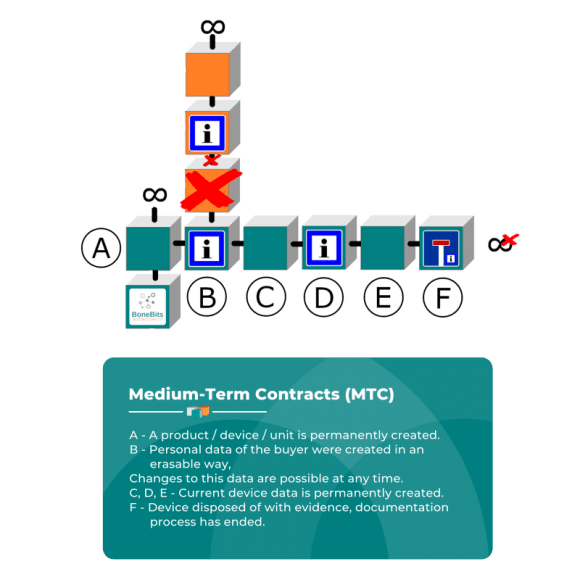
Medium-Term Contracts (MTC)
In the Smart Home and IOT area, personal data or data relating to the use are collected for durable products and utility articles during their life cycle. After expiry of their lifetime, these data are not necessary anymore and have to be partially erased.
A MTC applies in motor vehicles, maintenance agreements or in a Smart Refrigerator.
Motor vehicles
The life cycle of a motor vehicle may be documented in the decentralised data storage.
- A – A motor vehicle is permanently created
- B – Personal data of the buyer were created in a deletable way, the owner changed, the previous owner was deleted, the new owner was created in a deletable way
- C – First inspection was permanently registered, mileage.
- D – Accident was permanently created.
- E – Second inspection was created permanently, Service.
- F – The motor vehicle was disposed of with certificate, documentation process is completed.
The processes regarding the motor vehicle were registered permanently and clearly. This process may be used in many other application areas.
Smart Refrigerator
The life cycle of a Smart Refrigerator may be documented in the decentralised data storage.
- A – A Smart Refrigerator is permanently created
- B – Personal data of the buyer were created in a deletable way, the delivery address changed, the previous address was deleted, the new address was created in a deletable way
- C – Current order processes were permanently created.
- D – Maintenance process was permanently created.
- E – Current order processes were permanently created.
- F – The refrigerator was disposed of with certificate, documentation process is completed.
The processes regarding the device were registered permanently and clearly.
From the use of the aforementioned Medium-Term Contracts (STC) the following advantages result:
- Personal data were deleted
- All data regarding the subject were stored permanently
- Subject statistics may be created (failure statistics)
- Clear access of all participants to the process (online/app), e.g. in case of purchase of a used car before, vehicle history, previous damages
- Process carried out in a decentralised way without costs for maintaining, personnel, purchase and use of the own infrastructure (server/colocation/computing centre)
- Automatic resources scaling by the network
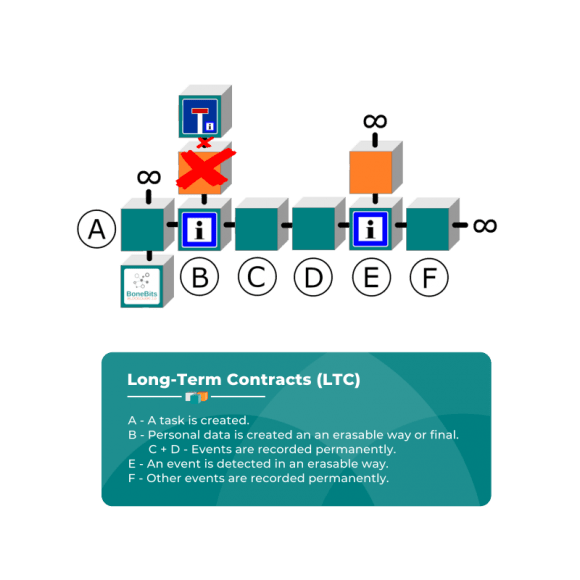
Long-Term Contracts (LTC)
Documentations in the LTC area are very well suitable to register timely long documentations. It includes in particular everything, which is related to the man or with real estate.
A LTC is applied in real estate, in citizens management for authorities or in the healthcare.
Reading services for accommodation units (Smart Home / IoT)
An accommodation unit may be run in a decentralised way in the area of ownership and house management for the current ancillary costs and energy consumptions. The documentation is connected firmly with the real estate. A change of the house management, the owners or tenants does not endanger the documentation.
- A – An accommodation unit was created.
- B – The previous tenant moved out, the personal data were deleted. The previous tenant’s account was permanently closed.
- C + D – Consumption data, ancillary costs or other things for 2 years were permanently registered.
- E – Information that a new tenant moves in, personal data were collected in a deletable way.
- F – The consumption data for the third year were permanently collected.
The decentralised data storage is suitable excellently especially in the Smart Home and IoT area in connection with the automatic consumption reading devices. The energy providers may document themselves or may document currently and daily updated for documentation on an arm of the blockchain of the accommodation unit. The tenant / owner has full transparency of the data online or via app at any time. Optimisation applications for energy costs saving could be also linked if necessary to the decentralised data storage through a port.
Citizens management for authorities
Authorities may manage tasks related to the citizens in a decentralised way. Depending on the project, other authorities may receive national, Europe-wide or worldwide access to the current data status. Inhabitants registration issues, registration of refugees, social benefits, Interpol, Office for Labour etc.
- A – A process (birth/registration/entry/search) is being created.
- B – Personal data are created/finally completed in a deletable way.
- C + D – Events are permanently collected (marriage, divorce, death etc.).
- E – Event is registered in a rewritable way (address changes etc.).
- F – Further events are permanently registered (relocation, etc.).
Due to the decentralised location, the information flow may be quickly read everywhere by the entitled authorities.
Healthcare system
Depending on the authorisation status, health insurance companies, hospitals and doctors may identify quicker and process diagnoses, previous illnesses and transfers. As owner of his data, the patient depending on his consent may authorise or not.
- A – A medical record is created.
- B – Personal data are created/finally completed in a deletable way.
- C + D – Events are permanently collected (illnesses, surgeries).
- E – Event is registered in a deletable way (medications, X-ray images).
- F – Further events are permanently registered (other procedures).
In this way a bit of control may be returned to the concerned person and nonetheless the fast data flow may be ensured after authorisation. Imaginable is also the application in the care of the elderly.
In the scope of the LTC there are as well many further application possibilities.
Energy Management
- Bottleneck management in the electricity distribution networks (e-mobility)
- Energy services for buildings & industry processes (maintenance)
- Registration of equipment in the register for the power and gas market (registry)
- Certification of proofs of origin
- Settlement of charges and levies (power)
- Termination and change of suppliers (power)
- Off-market wholesale (power)
- P2P trade between the clients of one power supplier
- Trade and allocation of network capacities (power)
- Landlord-to-tenant electricity
- Shared Investments in case of external landlord-to-tenant electricity
Further information:
Blockchain Studie Use Cases (DE)
Blockchain Integrierte Energiewende 02/2019 (DE)
Blockchain Executive Summery 02/2019 (DE)
Blockchain in der Energiewende 11/2016 (DE)
Blockchain in der Energiewende 11/2016 (EN)
Organisationen und Behörden
- Residents’ registration office
- Traffic office
- Police
- Court
- Hospital
- Branches
- Organisations
- Corporations
- NGO institutions
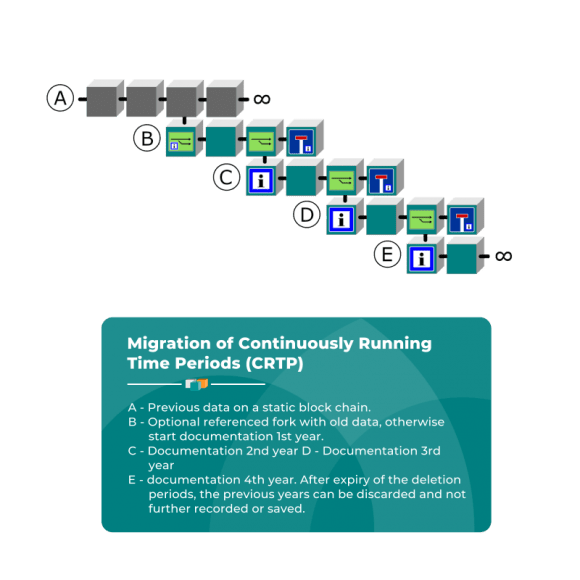
Migration of Continuously Running Time Periods (CRTP)
Data which have to be captures continuously are often subject to the statutory provided for erasure deadlines. The CRTP architecture is suitable to observe these periods. Due to a referenced merge process it allows also to migrate from an already used static infrastructure into a dynamic ecosystem.
CRTO is applied in accounting systems, business documents or credit agencies.
Accounting systems and business documents
Business documents are often subject to statutory retention periods. Here in particular in accordance with the German Commercial Code (6 years) and tax law (10 years). In order to fulfil these requirements old records have to be deletable after the expiry of the retention obligation. The process for that could be as follows:
- A – Current accounting on a static blockchain.
- B – Optional referenced fork at the old data pool, otherwise start documentation 9th year.
- C – Documentation 10. year.
- D – Documentation 11. year.
- E – Documentation 12. year. After expiry of the deletion periods the previous years may be discarded and not recorder or stored further.
After expiry of the retention period the old data may be deleted, because they are recorded with period obligation on separate blockchains. The following periods are respectively completed in themselves. The integrity is not influenced.
Credit agencies
Credit agencies record data about the creditworthiness of citizens and make it available in a decentralised way for requesting banks, insurers and companies. The concerned person may access the stored data about her at any time. After expiry of the record period the data have to be deletable.
- A – Current records on a static blockchain.
- B – Optional referenced fork at the old data pool, otherwise start documentation 1. year (consumer credit).
- C – Documentation 2. year (affidavit).
- D – Documentation 3. year.
- E – Documentation 4. year. After expiry of the deletion periods the previous years may be discarded and not recorder or stored further.
All participants may transparently access the record at any time and monitor the deletion securing.
Special advantages of the procedure developed by us (Dynamic Blockchain 2.0)
- Final ending of a blockchain.
- Entries may be deleted or changed.
- Smaller storage space requirement for chosen blockchain segments (defragmentation/Big Data).
- No continuous storage of old data or third-party pools necessary.
- Merge process of existing blockchains.
- Fork process possible in any block at any time.
Advantages of the dynamic network
- Direct provision and use of a new processing procedure.
- Fork-resistant, blockchain overarching network.
- Through all blockchains dynamically distributed computing power (hash power).
- Changing the node software in case of procedure changes is not necessary.
- Choice of the network structure (owned or shared network)
- Update / bug fix through Open Source network software development
- IR personnel outsourced
- No server park necessary
- No maintenance costs
Advantages of the dynamic procedural logic
- Relocation of processes in not publicly accessible areas.
- Free choice of the script or programming language.
- Software with procedural logic safe against manipulation.
- Adjustable, needs-based customised energy demand.
- Variable production quantity by the block creation (highest possible scaling).
- Reliable and economically reasonable transactions prioritisation.
- Proof Of Work, Proof Of Stake etc. may be applied parallel.
- All properties are freely combinable for individual adjustment to the own requirements (modular principle).
Advantages of the dynamic API
- Uncomplicated
- Compact commands create, change, delete & close
- newData
- newFork
- newMerge
- newInformation
- changeData
- deleteData
- closeChain
- pauseChain
Licenses
- Consulting
- Unique selling point
- Market edge
- Innovation
- License protection
Advantages of the blockchain generally
- Trust
- Integrity
- Safety
- Redundancy
- Transparency
- Decentralisation
- Revision safety
Further advantages result from own applications – BDMaaS (Blockchain Data Management as a Service) as API, APP, etc.
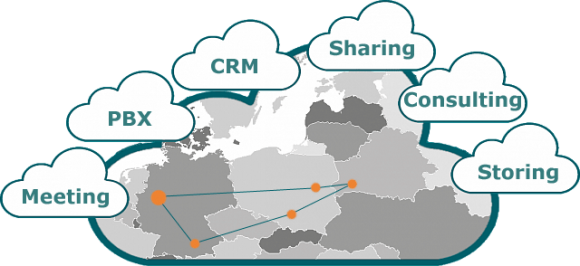
Team and services in the cloud
The registered office of our company is in Dortmund. Both shareholder and CEO reside in Dortmund and Munich. The software development is employed in Warsaw, the programmer team is in Brest and the web developers in Cracow.
As a modern cloud company, we use the possibility to employ highly qualified specialists outside our region as well. For that purpose we have an infrastructure adjusted to the situation in the cloud which connects all the employees with each other as they would be present physically in one room. All resources are commonly used through the cloud.
We receive visitors after appointment in our headquarters in Dortmund. If necessary, employees join the meeting via video conference.
CRM
The whole team is connected with each other through CRM. Both the project management as well as quick communication based on video, audio and text takes place there.
PBX
Through a modern hosted PBX, all team members on desktops as well as in mobile devices are connected with each other and also with external participants.
Storage
A company-wide through roles operated cloud storage is available highly redundant for all employees for all digitalised documents and data.
Meeting
Joint meetings in the team take place usually via video communication. In regular intervals, the team members meet also personally all together or regarding the project in various places. Meetings with interested parties and external participants take place individually depending on the project.
Sharing
The cloud infrastructure ensures that information and knowledge are shared with others in various ways. In the software development we rely on the proven, internationally applied software solutions like Jira or GitLab.
Consulting
Internal consulting takes place in the above mentioned ways.
This configuration type allows us to act quickly and purposefully.
QI 2023
Roll out Blockchain Data Management as a Service (BDMaaS).


QIV 2022
Beta Version Blockchain Data Management as a Service (BDMaaS).
QIII 2022
Start of main network.


QII 2022
Start of test network.
December 2020
Prototype as a live test on the website.


October 2020
Search and finding of first pilot projects and strategical partners from economy and research.
August 2020
Patent Publikation DPMA and International.


January 2020
International patent application.
March 2019
Development of licence concepts.


Februar 2019
DPMA patent application.
November, 5th 2018
Foundation of the BoneBits GmbH.


September 2018
Completion of conception.
February 2016
Continuous development and elaboration of possible solutions.


January 2015
Blockchain implementation idea in the own company.
Innovators & Early Adopters
The market for dynamic data storages based on blockchain is still young and it is waiting to be divided up. The innovators and the early adopters are those who ensure their place thanks to a new technology. By their early application and anticipatory action, the take first places in their industry, their market and their region. With that they ensure not only new business areas for themselves but in particular also the continuing existence of their company and the preservation of the client loyalty. The others are those who have to fight against client migration due to missing development and catch up. Now is the right time to make a good decision for the plans in your company.
We’ll support you in your plans with pleasure. With the licenses for the developed by us procedure adjusted exclusively for you and your project, your industry, your market or your region, we give you a perfect tool for your journey. Maybe a pilot project or a strategical partnership is the right start for you? Feel free to contact us. We will find the correct answers to your questions.
Universities, higher education institutions & education
New technologies are a good source for dissertations, master or bachelor theses. The dynamic data storage based on blockchain opens still niches for many disciplines where research works may be carried out. The public awareness and attractiveness of a new and modern technology branch is of great importance with exciting research results. Dry, boring and many times exhausted subjects there are yet enough. However, the really exciting and innovative subjects are rare. Now is a good possibility to see to this subject and to make an anticipatory decision.
We would support you with pleasure at the start and during the development of own projects for your discipline. Special free education licences for the developed by us procedure create no cost burden for your research. Do you have an idea for a project in your head already? Share it with us. Feel free to contact us.